
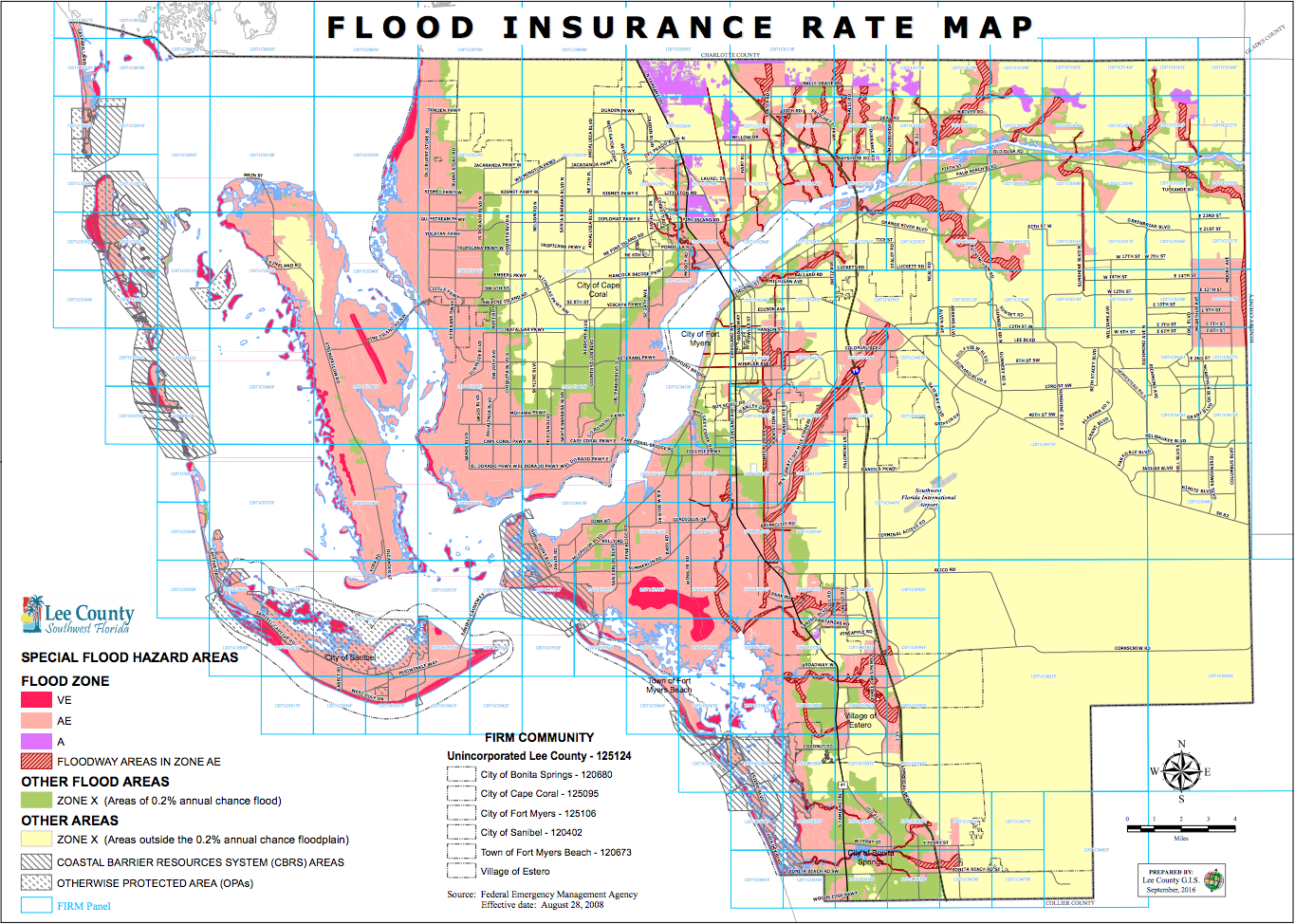
Zone V commonly refers to coastal regions, while Zone A is usually near a lake, river, stream or other body of water. Under the National Flood Insurance Program, residents located in these regions are required to buy flood insurance as part of their mortgage agreement.
Ae flood zone code#
To check if your home is in a flood zone, simply enter your address or ZIP code into FEMA’s online flood map service center. But how can homeowners determine whether they live in a flood zone and what level of risk they face?įEMA regularly creates and updates detailed flood zone maps that outline risks at the community level. In fact, almost 20% of all flood insurance claims and one-third of federal disaster assistance go to homeowners who live outside of high-risk zones, according to FEMA. While it’s true that flood hazard zones are more likely to experience a major flood event, almost everyone lives in an area with at least some risk.
.png)
During periods of above-average rainfall, local drainage systems can be overwhelmed and fail to direct water away from residential and commercial areas. Surface-water flooding: Also known as stormwater or rainfall flooding, this type of event is common in low-lying regions where rainwater and runoff can pool together. This type of flood cost Midwestern states more than $6.2 billion in 2019, The Chicago Tribune reported.ģ. Riverine floods occur when a body of water overflows its banks, either slowly or rapidly (flash flooding). Riverine flooding: Rivers and streams are also common sources of flooding, though these events are much harder to predict. Homes that are located along the coast can quickly become inundated with tidewaters, which is why FEMA considers these areas high risk.Ģ. Coastal flooding: Tropical storms and hurricanes can produce heavy storm surges, which may disrupt the tide and push ocean water inland. typically fall into one of three categories:ġ. According to the Penn Institute for Urban Research, floods in the U.S. This explains why coastal regions are often classified as high-risk zones, along with areas that are in close proximity to lakes, rivers and streams. In many cases, flooding is the result of severe weather events like hurricanes, tropical cyclones, heavy rainfall and storm surge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
